What to Consider When Selecting Miniature Ball Bearings
You need miniature ball bearings to help machines work well and last long. Picking the right ones spreads the load, lowers friction, and stops too much wear. If you choose ball bearings that fit your needs, you get smooth movement and less friction. Look at size, material, lubrication, and tolerance when picking. Things like temperature, humidity, and keeping out dirt matter for how long bearings last.
Picking the right bearing and lubricant helps stop early problems.
A good fit and taking care of bearings make them work better.
Key Takeaways
Pick the correct size and fit for miniature ball bearings. This helps them work well and stops them from wearing out too soon.
Choose materials such as stainless steel or ceramics. Think about where you will use them. This makes them last longer and work better.
Lubricate bearings often with the right grease or oil. This lowers friction and helps them last longer.
Think about how much weight and speed the bearings need. This keeps them from breaking and helps your machines work well.
Look at the manufacturer's specifications and size charts. This helps you make good choices when picking miniature ball bearings.
Miniature Ball Bearings Overview
What Are Miniature Ball Bearings
Miniature ball bearings are found in many small machines. They help parts move easily and reduce friction. You can tell them apart by their tiny size. Most have an outer diameter from 1mm to 30mm. Each bearing has an outer ring, an inner ring, a ball set, and a cage. These pieces work together to keep movement smooth and quiet.
Miniature ball bearings are much smaller than regular ball bearings.
Their shape lets parts move with little friction.
You see them used where space is limited and accuracy is important.
Choosing miniature ball bearings helps your equipment work better and last longer. It also helps lower noise and vibration in sensitive machines.
Why Precision and Fit Matter
Precision and fit are very important for miniature ball bearings. If you pick bearings with tight tolerances, you get less friction and cooler temperatures. This makes machines run faster and more smoothly. High precision bearings, like ABEC 7 or ABEC 9, work best for high-speed jobs.
High precision bearings have tighter tolerances for smoother movement.
These bearings cut down friction and keep things cool.
You need good miniature ball bearings for fast and long-lasting machines.
Miniature ball bearings are great for jobs needing low torque and high speed.
Some special types can spin up to 500,000 rpm.
When you choose the right fit and precision, you protect your equipment from wearing out too soon. You also help your machines stay quiet and work well.
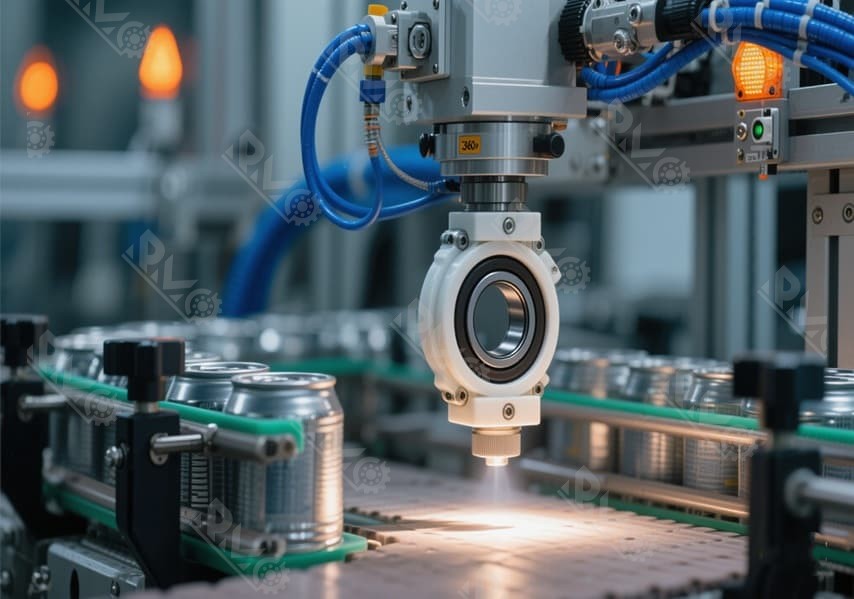
Common Applications of Miniature Ball Bearings
Miniature ball bearings are used in many fields. They fit in small spaces and need to be very precise. You find them in electronics, medical devices, robotics, automation, aerospace, and scientific tools. These bearings help machines work well and last longer.
Electronics and Medical Devices
Miniature ball bearings are inside many electronic gadgets. They help parts move in hard disk drives, fans, and printers. In medical devices, they help surgical tools and dental handpieces work well. Miniature deep groove ball bearings in these devices keep noise low and movement smooth. You need bearings that do not wear out fast and keep dust away. This makes devices safe and dependable.
Tip: Always make sure medical and electronic devices have good lubrication and seals. This stops dirt from getting in and helps your equipment last longer.
Performance Requirement
Description
Precision
Needed for smooth work in surgical tools and robots.
Material Selection
Stainless steel and ceramics last long and resist chemicals.
Lubrication
Cuts down friction and wear, making things work better.
Contamination Protection
Shields and seals keep out dust and liquids.
Noise Levels
Quiet bearings matter for sensitive devices.
Robotics and Automation
Robots and automation systems need miniature ball bearings to move exactly right. You use these bearings in robot arms and grippers for good control. Miniature deep groove ball bearings in automation help with fast movement and low torque. Miniature bearings for high-speed jobs help robots move quickly and smoothly. Their small size lets you put them in tight spots.
Miniature ball bearings lower friction and make machines more reliable.
Sealed bearings keep out dust in clean rooms and factories.
You get better results and longer life for your machines.
Aerospace and Instrumentation
Aerospace and scientific tools need bearings that work in tough places. You use miniature bearings for high-speed jobs in gyroscopes and navigation systems. These bearings must be light, strong, and work at high temperatures. Custom designs are often used in aerospace for special needs. Miniature ball bearings are used in lasers, measuring tools, and flight controls.
Challenge Type
Description
Advanced Materials and Coatings
Strong materials and coatings help in tough aerospace jobs.
Miniaturization and Lightweight Design
Small, light bearings save fuel.
High-Speed and High-Temperature
Bearings must work well when things move fast and get hot.
Customization
Special designs fit unique aerospace needs.
Miniature ball bearings help many industries. They let machines work with high precision, speed, and reliability.
Types and Selection of Miniature Ball Bearings
There are different types of miniature ball bearings. Each type works best for certain jobs. You need to know how each one works before you pick. The right choice depends on load, speed, and space. You should also think about the environment and how much care is needed.
Deep Groove Ball Bearings for Radial Loads
Miniature deep groove ball bearings are used a lot in small machines. They are good for radial loads, which push from the side. These bearings can also handle some axial loads, which push along the shaft. Miniature deep groove ball bearings are great for high speeds and low friction.
These bearings help machines carry more weight.
They support forces from both sides.
You get high-speed movement because the balls roll easily.
Miniature deep groove ball bearings are easy to take care of and keep clean.
You can use them in motors, fans, and big machines.
Miniature deep groove ball bearings fit well in small spaces. Their design is good for medical devices, robots, and electronics. They help things move smoothly and last longer. Picking the right miniature deep groove ball bearings makes your machines work better and need fewer repairs.
Tip: If you want less friction and more speed, use miniature deep groove ball bearings. They help machines stay quiet and last a long time.
Shielded, Sealed, and Open Bearings
You need to choose the right protection for your miniature ball bearings. Open, shielded, and sealed bearings all protect in different ways.
Feature
Open Bearing
Shielded Bearing
Sealed Bearing
Contaminant Protection
Low: No built-in protection from dust or moisture.
Moderate: Shields block large debris and dust.
High: Seals provide a tight barrier against dust and water.
Lubrication Retention
None: Needs outside lubrication.
Partial: Grease stays in better, but some can leak.
Excellent: Grease is sealed inside for the life of bearing.
Maintenance Needs
High: Needs regular cleaning and oil.
Moderate: May need some re-lubrication.
Minimal: Usually maintenance-free.
Open bearings are best for clean places where you can add oil often. Shielded bearings keep out bigger dirt and hold grease better. Sealed bearings give the most protection and need the least care. Think about where you will use the bearing and how much time you want to spend on care.
Specialty Bearings and Their Uses
Some jobs need special miniature ball bearings. These have features for tough or strange tasks. Thin-section ball bearings fit in very small spaces and help lower weight. You see them in medical tools and robots. They can handle both radial and axial loads.
Here are some examples of specialty miniature ball bearings and where you might use them:
Industry
Specific Use
Outcome Metrics
Medical Devices
Imaging equipment, surgical robots
Longer device life, less maintenance, safer for patients
Aerospace Components
Navigation, gyroscopes, satellites
Better reliability, lighter weight, longer service
Consumer Electronics
Smartphones, tablets, wearables
Better performance, smoother user experience
Robotics and Automation
Robotic joints, actuators
Faster cycles, more precision, less downtime
Drones and Unmanned Vehicles
Drone motors, gimbals
More stable flight, longer battery life, clearer images
Look at the features of each bearing before you pick. Some use stainless steel or ceramics for better results. Others have coatings to stop rust or heat. When you focus on the selection of miniature ball bearings, your machines work well in any place.
Note: Specialty bearings can cost more, but they last longer and need less care. This can save you money over time.
How to Choose the Right Bearing
To pick the right miniature deep groove ball bearings, match your needs to the features. Here are some things to check:
Design: Shape and size change how much weight it holds and how fast it spins.
Materials: Stainless steel does not rust. Chrome alloy steel lasts longer with heavy use.
Shields and Seals: These keep grease in and dirt out. Seals protect better but can make turning harder.
Cages: These hold the balls in place. The right cage helps with speed and heat.
ABEC Grade: This shows how exact the bearing is. Grades 3 and 7 are good for most jobs.
Radial Play: This is the small space inside the bearing. It helps with heat and fit.
Lubricant: Grease works best for most small bearings. It stays in place and does not leak much.
Alert: Always match the bearing’s features to your machine’s needs. The right choice helps your bearing work better and last longer.
If you pay attention when picking miniature ball bearings, you avoid problems like early wear or machine trouble. The right bearing gives you the best results, whether you use it in medical devices, robots, or drones. Miniature ball bearings help your machines move smoothly, quietly, and reliably in any job.
Key Factors in Selecting the Right Miniature Ball Bearings
When you pick miniature ball bearings, you should think about a few important things. These things help you choose the best bearing for your job and make it work better. You need to look at size, materials, how much weight it can hold, lubrication, and where it will be used. If you pay attention to these, you can stop problems and get good results.
Miniature Bearing Size Chart and Fit
You should use a miniature bearing size chart when picking bearings. This chart shows the outer diameter, inner diameter, and width. These numbers help you find the right size for your job. If you choose the wrong size, the bearing might not fit or work right. The size chart also lets you compare different bearings fast.
A good fit means the bearing will not slip or move. This helps your machine run well and stops damage. You can use the size chart to check all the sizes before you buy. Always pick the right size for your job to get the best results.
Tip: Always check the miniature bearing size chart before you buy. This easy step can help you save time and money.
Material Choices: Steel, Stainless, Ceramic
You should think about what the bearing is made of when you pick one. The material changes how long the bearing lasts and if it can handle rust or chemicals. Here are some things that change how well it works:
Corrosion Resistance: Some materials do not rust as fast. This helps the bearing last longer in wet or rough places.
Hardness and Wear Resistance: Harder materials can take more stress and last longer.
Thermal Properties: Some materials work better in hot or cold places. This keeps the bearing strong.
You can find miniature ball bearings made of steel, stainless steel, or ceramic. Steel bearings are good for most jobs. Stainless steel does not rust and works in wet or chemical places. Ceramic bearings are light and strong. They are good for high precision and low friction jobs. Always pick the right material for your job to get the best results.
Load Capacity and Types
Load capacity is one of the most important things to think about. You need to know how much weight your bearing will hold. The static load rating shows how much weight the bearing can take before it changes shape. This is important for machines that do not move much.
The dynamic load rating shows how much weight the bearing can take while moving. This rating tells you how long the bearing will last with a steady load. You should always check both ratings before you pick a bearing.
If you pick a bearing that cannot hold enough weight, it can wear out fast or break. Too much weight can hurt the bearing and make it less reliable. You also need to think about preload, speed, and how the weight changes when you use it. These things all change how long your bearing will last.
Picking the wrong load can cause wear and damage.
Too much weight can break the bearing early.
Not enough oil, bad alignment, and too much weight are main reasons for problems.
Lubrication and Maintenance Needs
Lubrication is another important thing to think about. You need to pick the right oil or grease for your job. Grease works well for most miniature ball bearings, especially in closed places. Oil is better for fast jobs because it lowers friction.
You should not use too much or too little oil or grease. Too much can make the bearing fail. Too little can make it hot and wear out. Always follow the care plan for your bearings. This helps them work well and last longer.
Grease is common and works for most jobs.
Oil is best for fast or hot jobs.
Good lubrication is needed for low friction and high precision.
Alert: Check your bearings often and add oil or grease if needed. This easy step can stop many problems.
Environmental and Operating Conditions
You need to think about where you will use your miniature ball bearings. Wet air, dust, and hot or cold places all change how well they work. Wet air can make them rust and wear out. Dust can hurt the bearing and mess up the oil or grease. Hot or cold can change how the bearing and oil or grease work.
You can use stainless steel or ceramic miniature ball bearings in wet or dirty places. Special coatings and good seals help keep out water and dust. Always pick the right bearing for your job and where you will use it.
Wet air can make bearings rust and wear out fast.
Hot or cold can change how the bearing and oil or grease work.
Dust and dirt can hurt the bearing and make it work worse.
Use rust-proof materials and good seals for tough places.
When you think about these important things, you get the best results for your job. You help your machines last longer, move faster, and work better. Always use a size chart, pick the right material, check the weight it can hold, use the right oil or grease, and think about where you will use it. These are the most important things for miniature ball bearings.
Matching Miniature Ball Bearings to Your Application
Assessing Application Demands
You need to look at your application closely before you pick miniature ball bearings. Start by thinking about the load. Ask yourself how much weight the bearing will carry and what kind of force it will face. Next, check the speed and precision your machine needs. Some jobs need bearings that spin very fast or move with great accuracy. The environment also matters. Dust, water, or heat can change how well the bearing works.
Load conditions: Think about the weight and direction of the force.
Speed and precision: Decide how fast and accurate your machine must be.
Environmental influences: Look for dust, moisture, or chemicals that could harm the bearing.
You should also look at how the bearing fits with other parts. Make sure the size matches your space. Think about how easy it is to mount and take care of the bearing. Good planning helps you avoid problems later.
Balancing Performance and Cost
You want miniature ball bearings that work well but do not cost too much. Standard bearings often cost less than custom ones. They also arrive faster. Sometimes, you can pick a less expensive material with a special coating or heat treatment. This can give you the performance you need without a high price. Tight tolerances make bearings more precise, but they also raise the cost. Each extra decimal place in the tolerance can double the price. You should only pay for the precision your job really needs.
Tip: Choose standard miniature ball bearings when possible. Save custom options for special needs.
Using Manufacturer Specifications
Always check the manufacturer’s specifications before you buy miniature ball bearings. Look at the bearing type. Ball bearings work best for high speeds. Check the size and structure to make sure they fit your space and speed needs. The cage material matters too. Solid cages let the bearing spin faster. Lubrication is key for smooth movement and long life. Make sure the lubricant matches your speed and temperature needs.
Here is a checklist to review:
Bearing type and speed rating
Size, structure, and fit
Cage material and design
Lubrication type and compatibility
Protection against dust and moisture
Environmental limits like temperature and humidity
If you follow these steps, you will find miniature ball bearings that fit your job and last longer.
Common Mistakes in Selection and Troubleshooting
Overlooking Size and Fit
Some people think any bearing will work. But if you do not check size and fit, you can have big problems. The wrong size might not fit or move right. A bad fit can make too much stress and friction. This can make the bearing break early. The table below shows what can happen if you do not check size and fit:
Factor
Explanation
Preloading
Not checking clearance can put stress on the bearing parts.
Increased Friction
Extra stress makes more friction and heat, which breaks down lubricant.
Creep
Loose fits cause movement, heat, and wear particles, leading to vibration and failure.
Fretting Corrosion
Tiny movements create wear particles that turn into abrasive powder.
Stress Concentration
Bad fit causes stress in one spot, making the bearing wear out faster.
Tip: Always use a size chart and check the fit before you put in miniature ball bearings.
Ignoring Load or Speed Requirements
If you do not check load and speed, your bearings can get damaged. Too much weight or speed can make friction and wear happen fast. This can break the bearing early. The table below shows what can go wrong:
Consequence
Description
Excessive Friction
Bearings get too hot and wear out quickly.
Material Fatigue
Parts weaken and break from too much load.
Premature Failure
Bearings stop working before their expected life.
Increased Maintenance Costs
You spend more time and money fixing problems.
Uneven Load Distribution
Rolling parts shift, causing more wear.
Neglecting Lubrication and Maintenance
Lubrication helps miniature ball bearings move smoothly. If you forget to add grease or oil, friction and wear get worse. You should not use too much or too little. Good lubrication makes a film that keeps metal parts apart. If you see heat, noise, or shaking, the lubrication may be bad. You need to check and add oil or grease often.
Good lubrication lowers friction and wear.
It makes a film that protects moving parts.
Watch for overheating, strange sounds, and shaking.
Check lubrication when needed, not just by the calendar.
🛠️ Regular maintenance helps your bearings last longer.
Troubleshooting Premature Wear
Premature wear can stop your machine and cost money. You need to know the signs and fix problems fast. The table below shows common causes, symptoms, and how to fix them:
Cause of Premature Wear
Symptoms
Corrective Procedures
Lubrication Failure
Brown or blue marks on balls and tracks
Lubricate key areas and watch temperature.
Contamination
High vibration and wear
Keep work areas clean and store bearings safely.
Misalignment
Uneven wear paths
Remove dirt and burrs, align parts correctly.
Overloading
Spalling and overheating
Lower the load or redesign for more capacity.
Shock Loads
More vibration and wear
Avoid rough handling and impacts.
Poor Handling
Severe wear paths
Use proper installation and gentle force.
You can stop most problems by picking the right miniature ball bearings, checking fit, and doing regular maintenance.
Maintenance Tips for Miniature Ball Bearings
Installation Best Practices
You can make your miniature ball bearings last longer by following good installation steps. Always keep the bearings and the work area clean. Do not wash new bearings because they come pre-lubricated. Store them in a dry place and keep them in their package until you need them. Handle each bearing with care and use clean tools. Before you start, check the shaft and housing for a good fit. Mount the bearing correctly and make sure the outer race sits square in the housing. Never hammer directly on a bearing. Apply even pressure and check for noise or rough movement after installation.
Installation Checklist:
Clean work area and tools.
Inspect shaft and housing.
Use proper lubrication.
Mount bearing with even pressure.
Check for correct fit and smooth operation.
Tip: Always use the same type of bearing when replacing to keep performance steady.
Routine Inspection and Cleaning
You should inspect your bearings often. Heavy-duty or always-running machines need checks every week. Machines in tough places may need daily checks. For standard machines, look once a month. If you use a machine only a little, check every few months. After any repair, inspect the bearing soon.
When cleaning, use a brush to remove dirt and grease. Rotate the bearing slowly in clean oil or kerosene. Dry it well and add anti-corrosion oil right away. Always check for cracks, rust, or rough spots. Listen for odd sounds and check if the bearing feels hot.
Lubrication Schedules
Lubrication keeps miniature deep groove ball bearings running smoothly. Use the type and amount of lubricant the maker suggests. Grease works for most jobs, but oil is better for high-speed work. Check the lubricant often and replace it if it looks dirty or dry. Too much or too little can cause problems. Stick to a regular schedule to avoid trouble.
Lubrication Type
When to Use
How Often to Check
Grease
Most applications
Monthly
Oil
High-speed jobs
Weekly
Signs of Wear and Replacement Timing
You need to watch for signs that your bearing needs replacing. Look for cracks, rust, or leaks. Feel for rough spots when you turn the bearing. Listen for new noises or check if the bearing gets hot. If you see any of these signs, replace the bearing right away. Quick action can save your machine from bigger problems.
Note: Early replacement of worn bearings helps prevent machine failure and costly repairs.
You should think about size, material, load, lubrication, and fit. Always look at a size chart before you buy bearings. Read the manufacturer’s instructions to help you choose. Know what your machine needs before you pick a bearing. This helps you get the best one for your job.
Tip: Check what your machine needs before you buy. Picking the right bearing helps your machine work better and saves money.
FAQ
What is the smallest size for miniature ball bearings?
You can find miniature ball bearings as small as 1mm in outer diameter. These tiny bearings fit in compact devices like medical tools and electronics.
How do you know which material to choose?
Stainless steel resists rust. Ceramic offers low friction and light weight. Chrome steel works well for most machines. You should match the material to your environment and performance needs.
How often should you lubricate miniature ball bearings?
Check your bearings every month. Add grease or oil if you see dryness or hear noise. High-speed machines may need weekly checks.
Can you reuse a miniature ball bearing after removal?
You should not reuse bearings if you see wear, rust, or damage. Always inspect for cracks or rough spots. Replace old bearings to keep your machine safe.


 Aerospace
Aerospace Food & Beverage
Food & Beverage Medical
Medical Robotics
Robotics Industrial Bearings
Industrial Bearings Building Materials
Building Materials Electric Motor Quality Bearings
Electric Motor Quality Bearings Sports, Recreation & Hobby
Sports, Recreation & Hobby







 August 12, 2024
August 12, 2024

 March 18, 2025
March 18, 2025
 December 12, 2025
December 12, 2025
 December 05, 2025
December 05, 2025
 November 28, 2025
November 28, 2025
 November 19, 2025
November 19, 2025
 November 13, 2025
November 13, 2025
 November 06, 2025
November 06, 2025
 October 31, 2025
October 31, 2025
 October 21, 2025
October 21, 2025
 October 17, 2025
October 17, 2025
 October 11, 2025
October 11, 2025












 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported